What is Layer 7?
Layer 7, or the application layer, is the highest layer in the OSI model. It directly interacts with the software on computers and devices, enabling communication between users and applications. Everyday activities such as sending emails, uploading or sharing files, and browsing websites all take place at this layer.
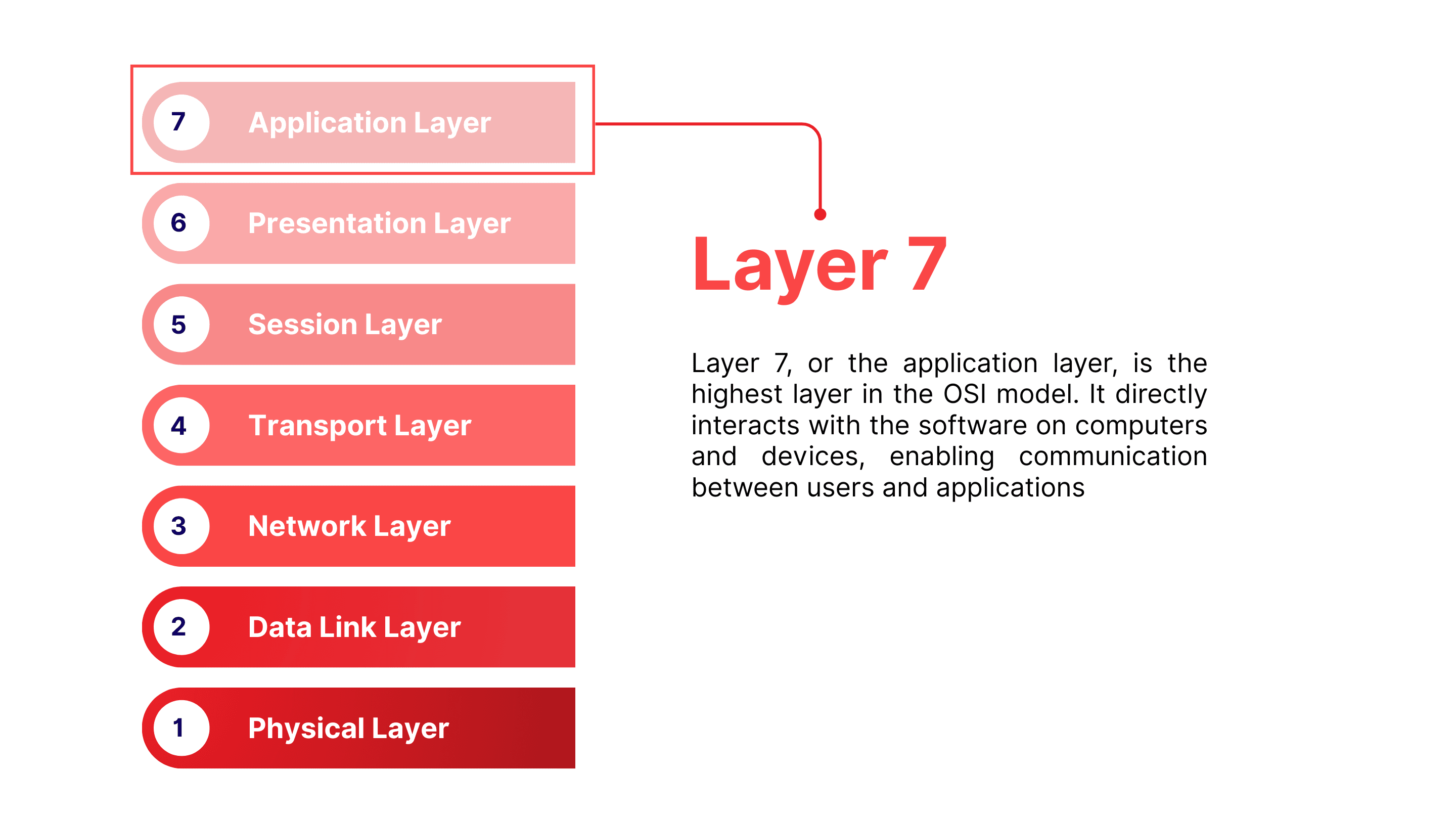
The application layer converts application-level information into data that can be transmitted across the network, while also processing incoming data to display it correctly. Because it deals directly with content, Layer 7 is frequently the target of sophisticated attacks. A common example is a DDoS attack, where attackers exploit protocols such as HTTP or HTTPS to overload servers and disrupt services.
What are the functions of Layer 7?
At the application layer, data is not only transmitted but also processed to fulfill user and application requests. Information is formatted, validated, and secured before it reaches its destination. Key functions of Layer 7 include:
- Managing application communication: Organizing and formatting data to ensure accurate exchange between applications.
- Data translation: Converting data between different formats so that systems remain compatible and work seamlessly.
- Authentication and security: Applying login, verification, and encryption processes to protect data during transmission.
- Supporting multiple protocols: Using protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, and DNS to meet various connectivity needs.
- Access control: Accepting or rejecting requests based on policies and security rules.
What is a Layer 7 DDoS attack?
A Layer 7 DDoS attack is a type of distributed denial of service that directly targets the application layer. Unlike attacks at Layer 3 or Layer 4, which often saturate bandwidth, this method sends a massive number of seemingly legitimate HTTP or HTTPS requests, forcing servers to process them until resources are exhausted.

Key characteristics of Layer 7 DDoS attacks include:
- Difficult to detect, since attack traffic looks almost identical to normal user activity.
- Primarily consumes processing resources such as CPU, RAM, or database connections.
- Often targets specific points of an application, such as APIs, login forms, or search functions.
Because of their complexity and stealth, effective defenses require Layer 7 firewalls and specialized DDoS protection that can analyze, identify, and block malicious traffic at the application layer before it impacts the system.
Common types of Layer 7 DDoS attacks
Layer 7 attacks typically exploit the core functions of websites or online services. The most common forms include:
- HTTP Flood: Attackers send a flood of HTTP requests to a web server. Each request looks valid but consumes processing power, eventually slowing down or crashing the server.
- Slowloris: Instead of flooding requests, this method opens multiple HTTP connections and sends data extremely slowly, keeping connections “hanging” and consuming server resources.
- SQL Injection: Malicious SQL commands are injected into web forms or URL parameters to manipulate databases, steal information, or delete critical data.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Malicious scripts are injected into web pages to run in a user’s browser, often used to steal cookies, hijack sessions, or display fake content.
- XML-RPC Abuse: Exploits XML-RPC interfaces (commonly found in CMS platforms like WordPress) to send mass automated requests. A single connection can generate hundreds or thousands of commands, quickly overwhelming the system.
All these methods exploit weaknesses at the application layer, making them hard to detect with standard network-layer defenses. Specialized Layer 7 anti-DDoS solutions are therefore essential for analyzing traffic behavior and blocking attacks before they impact services.
Consequences of Layer 7 DDoS attacks
If not detected and mitigated quickly, Layer 7 attacks can cause severe consequences that directly impact business operations and reputation:
- Service disruption: Websites, APIs, or online applications may crash or respond unusually slowly, frustrating users and driving them to competitors.
- Brand damage: Extended downtime or slow performance erodes customer trust, especially in industries where reliability is critical such as finance, healthcare, or banking.
- Financial losses: Revenue drops due to halted transactions, coupled with high costs for recovery, infrastructure upgrades, and new defenses.
- Security risks: In some cases, Layer 7 DDoS is used as a smokescreen to distract IT teams while attackers exploit vulnerabilities and steal sensitive data.
Difference between Layer 7 attacks and Layer 3/4 attacks
Each OSI layer handles data differently, and so do the attacks that target them:
- Layer 3 (Network Layer): Attacks target the network infrastructure, often using techniques like UDP flood or ICMP flood to saturate bandwidth and block communication.
- Layer 4 (Transport Layer): Attacks focus on TCP or UDP connections, exhausting the server’s ability to handle requests. A typical example is a SYN flood, where incomplete handshake requests overwhelm server resources.
- Layer 7 (Application Layer): Attacks target web applications, APIs, or online services directly. Malicious requests look like normal traffic but are delivered at high volume and frequency, overloading the system.
From an attacker’s perspective, Layer 7 DDoS is harder to detect than lower-layer attacks because traffic closely mimics real user behavior. Effective defense requires intelligent filtering systems at the application layer that analyze traffic behavior instead of relying solely on IP addresses or static signatures.
VNETWORK’s Layer 7 DDoS Protection Solutions
VNETWORK provides AI Web Application Firewall (AI-WAF), a solution designed to detect and block Layer 7 attacks in real time. Key features include:
- Real-time threat prevention: AI-driven contextual and behavioral analysis, with dynamic rule engines to stop attacks like Injection, Brute Force, Defacement, and the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities.
- Layer 7 DDoS protection: Cloud WAF inspects all traffic, detecting and filtering malicious requests to prevent overloads and downtime.
- Enhanced global performance: A distributed CDN infrastructure supports edge caching, load balancing, and latency reduction, ensuring fast responses even during traffic spikes.
- Modern security and connectivity: Automated SSL/TLS certificates, HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 compatibility, and secure, reliable connections for users worldwide.
FAQ – Common questions about Layer 7 and application-layer security
- Why is Layer 7 a common target for hackers?
Because it processes user data and requests directly, it can be exploited through functions like search, login, or APIs. - How can you detect a Layer 7 DDoS attack early?
Warning signs include slow server responses, sudden spikes in HTTP/HTTPS requests, and unusual CPU or RAM usage. - Is Layer 7 related to API security?
Yes. Since APIs operate at the application layer, any vulnerabilities or attack traffic targeting APIs fall under Layer 7 attacks. - Does Layer 7 always use HTTP/HTTPS?
No. It also supports protocols like SMTP, FTP, and DNS depending on the type of service. - Can businesses secure Layer 7 without using a WAF?
Basic measures such as rate limiting, CAPTCHA, or IP filtering can help but remain limited. A WAF provides more comprehensive detection and protection. - Does Layer 7 security affect user data protection?
Yes. Since this layer often handles sensitive information like personal data, passwords, and payment details, securing it is crucial for safeguarding user privacy.
Conclusion
Layer 7 DDoS attacks are increasingly sophisticated, targeting the logic and resources of applications to disrupt services and cause serious business damage. Proactive defenses at the application layer are essential for maintaining availability, security, and performance.
VNETWORK’s AI-WAF provides real-time detection and mitigation of Layer 7 attacks, helping businesses safeguard infrastructure, protect their reputation, and ensure smooth user experiences—even under extreme traffic conditions.
Contact us via hotline (+84) 28 7306 8789 or email contact@vnetwork.vn to secure your system against threats and guarantee uninterrupted services.
.jpg)