1. Overview of the Data Law 2024
Before delving into specific provisions, enterprises need a clear understanding of the law’s legislative foundation, scope, effective date, and applicable entities. This foundational knowledge empowers organizations to proactively develop data governance and security strategies aligned with the new legal framework.

1.1. Basis and Effective date
- Law No. 60/2024/QH15 was passed by the 15th National Assembly on November 30, 2024.
- It becomes effective on July 1, 2025.
- The document comprises 5 or 6 chapters (sources vary, citing 5 chapters and 46 articles).
1.2. Scope and Applicable entities
The law governs:
- Digital data, including collection, creation, storage, processing, sharing, and utilization across all domestic sectors.
- Activities related to building, developing, protecting, governing, processing, and using data.
- National databases, national data centers, data products/services, and state management of data.
- Rights, obligations, and responsibilities of agencies, organizations, and individuals involved in data activities.
The law does not apply to:
- Classified national data or data in defense and security domains, where specialized laws provide detailed regulations (provided they align with the Data Law’s principles).
2. Key innovations and Critical provisions
The Data Law 2024 (Law No. 60/2024/QH15) establishes a legal foundation for data governance and exploitation while introducing groundbreaking innovations. These provisions aim to foster a secure, transparent data environment while driving national digital transformation.
Below are key focus areas enterprises and organizations must prioritize for compliance and implementation.
2.1. Principles for Building, Governing, and Using Data
The law establishes foundational principles for all data activities:
- Compliance with the Constitution and related laws, protecting human and citizen rights.
- Transparency, equality, and equitable access to data exploitation.
- Data collection must be accurate, inheritable, and ensure integrity, reliability, security, and safety.
- Data protection must occur concurrently with development, avoiding neglect of safety during exploitation.
- Data storage, connectivity, sharing, and utilization must be efficient, simple, and convenient for individuals and organizations accessing public services or administrative procedures.
These principles serve as a guiding compass for organizations designing data systems and delivering digital services without legal violations.
2.2. Prohibited actions
The Data Law explicitly outlines prohibited actions to safeguard national, public, and individual/organizational legal interests:
- Exploiting data to infringe on national interests, ethnic groups, security, public order, or other lawful rights.
- Illegally obstructing data processing/governance or attacking, seizing, or damaging databases.
- Falsifying, intentionally distorting, destroying, or losing data in state or political-social organization databases.
- Deliberately providing inaccurate data or failing to submit data as required.
Enterprises should implement monitoring, auditing, access control, and incident response protocols to avoid violations.
2.3. Establishing the National Data Center and Integrated National Database
A notable feature of the Data Law is the establishment of the National Data Center and Integrated National Database—critical infrastructure for a digital government:
- The National Data Center stores and manages national data infrastructure, meeting international standards with high security and redundancy.
- The Integrated National Database, managed by the National Data Center, facilitates data connectivity and sharing across agencies and specialized systems.
- Open, shared, and private data must be collected, updated, and synchronized into the Integrated National Database.
- The National Data Portal, public service portal, integration platform, and data-sharing platform connect these systems.
This requires enterprises sharing data with government or public systems to meet technical, security, and format standards mandated by the law.
H3: 2.4. Risk management and Data protection
The Data Law 2024 emphasizes risk assessment in data processing and organizations’ data protection obligations:
- Risks include privacy, cybersecurity, access, identification, and other processing-related threats.
- State agencies must identify and establish early-warning mechanisms for data risks.
- Data controllers (e.g., enterprises or organizations) must self-assess risks, implement protective measures, and notify data subjects or relevant entities in case of incidents.
- National and specialized databases must adhere to technical standards and regulations outlined in the law.
This presents an opportunity for enterprises to adopt a risk-based approach, building proactive data security processes to ensure compliance and enhance trust with customers and partners.
3. Impact of the Data Law on Technology enterprises and Network service providers
Upon its effective date, the Data Law will reshape how enterprises manage, share, and protect user data.
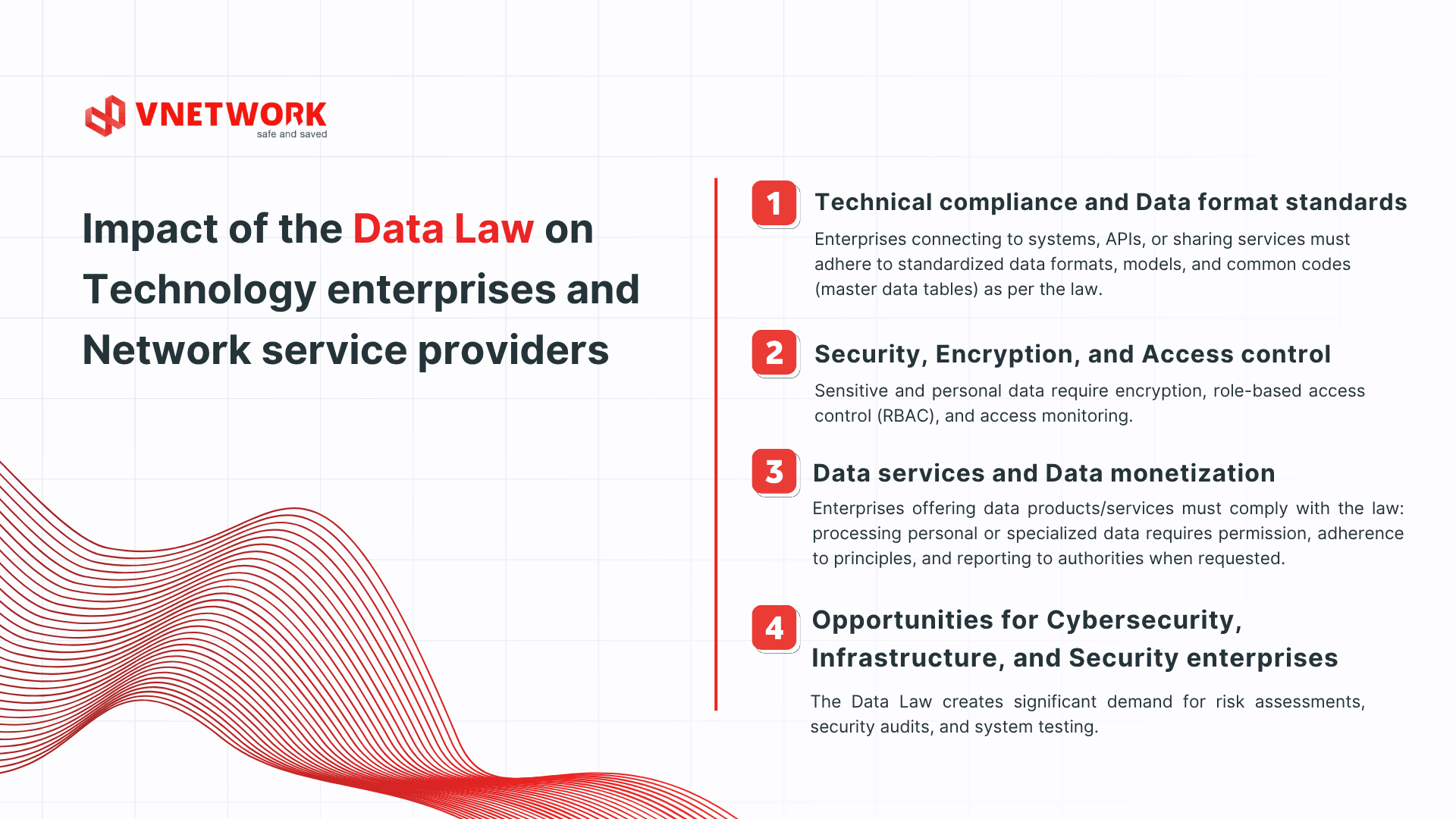
3.1. Technical compliance and Data format standards
- Enterprises connecting to systems, APIs, or sharing services must adhere to standardized data formats, models, and common codes (master data tables) as per the law. (Avoid redundant data collection where equivalent data exists.)
- Integrated systems across modules, APIs, web/app platforms must ensure secure, protocol-compliant connections with strict access controls to avoid legal breaches during data sharing or usage.
3.2. Security, Encryption, and Access control
- Sensitive and personal data require encryption, role-based access control (RBAC), and access monitoring.
- Systems must include alerts and response protocols for breaches or data leaks, with procedures to notify data subjects or regulatory bodies as required.
- Compliance with international security standards like ISO 27001 and ISO 20000-1 offers a competitive edge for certified enterprises.
3.3. Data services and Data monetization
- Enterprises offering data products/services must comply with the law: processing personal or specialized data requires permission, adherence to principles, and reporting to authorities when requested.
- When providing data services to organizations or users, enterprises must transparently disclose usage terms, purposes, withdrawal rights, and complaint mechanisms if data is mishandled.
3.4. Opportunities for Cybersecurity, Infrastructure, and Security enterprises
The Data Law creates significant demand for:
- Risk assessments, security audits, and system testing.
- Data protection solutions, encryption, monitoring, intrusion detection/prevention (IDS/IPS), and SIEM/SOC systems.
- Compliance services, data audits, and IT legal consulting.
- Cloud platforms and secure data infrastructure meeting national standards.
For VNETWORK, this is a pivotal moment to solidify its position as a comprehensive security solutions provider, supporting enterprises in adhering to the Data Law.
4. Roadmap for enterprise compliance with the Data Law 2024
To meet the Data Law 2024 (Law No. 60/2024/QH15) requirements, enterprises must develop a structured roadmap—from assessment to operation and compliance monitoring. This is not just a technical endeavor but a comprehensive data governance strategy ensuring safety, security, and transparency in the digital era.
- Assess current data status: Identify data classification, data flows (collection, processing, sharing), and risk points.
- Evaluate risks and plan data protection: Implement standardization, encryption, access control, monitoring, logging, and alerting.
- Design compliant data architecture: Use common code models, integrate standard formats, and ensure compatibility with national systems if required.
- Conduct security testing and compliance audits: Perform penetration testing, security audits, and verify adherence to Data Law principles.
- Deploy security solutions: Utilize VCLOUD for storage, VNIS for web/app/API protection, and EG-Platform for email security.
- Monitor, respond to incidents, and report: Establish incident response, alerting, and breach notification procedures.
- Train and raise employee awareness: Define access rights and provide Data Law training for operations, development, and security teams.
- Review and improve periodically: Update risk assessments and adjust solutions/processes based on operational insights.
Effective roadmap execution requires collaboration with technology partners offering end-to-end expertise in assessment, architecture design, and security compliance. This is why VNETWORK emerges as a trusted ally, enabling enterprises to comply while optimizing digital operations.
5. VNETWORK - Partnering with enterprises for Data Law 2024 compliance
Successfully implementing the Data Law 2024 (Law No. 60/2024/QH15) roadmap requires more than internal processes—it demands advanced infrastructure and security solutions. As a leading Science and Technology Enterprise in infrastructure, transmission, and cybersecurity, VNETWORK delivers a comprehensive ecosystem to help organizations store, process, and protect data in line with legal standards while maximizing digital efficiency.
 (3).jpg)
5.1. VCLOUD Solution
- A cloud-native infrastructure achieving Tier III certification, ensuring 99.997% uptime for stable, continuous enterprise data storage.
- Integrates CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) for version management, automated testing, and accelerated deployment while maintaining data security.
- Complies with international standards like ISO 27001, ensuring legal compliance for storing and processing personal or sensitive data.
5.2. Comprehensive Web/App/API Security Solution - VNIS
- An AI-powered security system with SOC (Security Operations Center) for early detection of ransomware, DDoS attacks, vulnerabilities, and real-time response.
- Secures API access, implements TLS/SSL communication layers, validates inputs, and protects against OWASP Top 10 attacks—reducing Data Law violation risks during data processing and sharing.
- Offers risk assessments, penetration testing, and log monitoring to meet legal risk evaluation obligations.
5.3. AI & Machine learning Email Security Solution - EG-Platform
- The world’s only email security solution fully compliant with ITU-T X.1236 standards, protecting against phishing, ransomware, and APT attacks.
- Leverages AI and machine learning to detect anomalies, safeguard mailboxes, and provide early warnings for email-based threats.
- As a critical data exchange channel, EG-Platform ensures Data Law compliance for customer, employee, and partner communications, preventing personal data leaks via email.
With over 12 years of cybersecurity expertise, VNETWORK holds Science and Technology Enterprise certification (No. 59/DNKHCN), ISO 27001 and ISO 20000-1 certifications, and Gartner recommendations. Beyond technology, VNETWORK offers consulting, roadmap development, monitoring, testing, and 24/7 technical support to ensure robust data system security.
Experience VNETWORK’s VCLOUD, VNIS, and EG-Platform solutions at: https://www.vnetwork.vn/vi-VN/contact-us.
6. Conclusion
The Data Law 2024 (Law No. 60/2024/QH15) marks a significant legal advancement, establishing a framework for data governance, protecting individual rights, and promoting a transparent, secure digital ecosystem. For technology, network, and security enterprises, compliance is not merely a legal duty but a chance to build trust and enhance brand value.
VNETWORK, with its VCLOUD, VNIS, and EG-Platform solutions, commits to partnering with enterprises in implementing the Data Law 2024—from infrastructure design and system security to compliant data processing workflows.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about the Data Law 2024 (Law No. 60/2024/QH15)
1. When does the Data Law 2024 take effect?
Law No. 60/2024/QH15 takes effect on July 1, 2025, following its passage by the National Assembly on November 30, 2024.
2. What activities does the Data Law regulate?
The law governs the collection, creation, storage, processing, connectivity, sharing, exploitation, and management of digital data, including national database systems.
3. What must technology enterprises do to comply with the Data Law?
They must assess data risks, establish access control and security processes, encrypt data, conduct security audits, and ensure lawful data connectivity and sharing.
4. Does the Data Law mandate a National Data Center?
Yes, it requires the establishment of a National Data Center and Integrated National Database to connect, store, and share data across government and specialized systems.
5. How does VNETWORK assist enterprises with Data Law compliance?
VNETWORK provides VCLOUD (secure cloud infrastructure), VNIS (web/app/API security), and EG-Platform (email security) solutions, along with consulting, risk assessments, and 24/7 monitoring support.