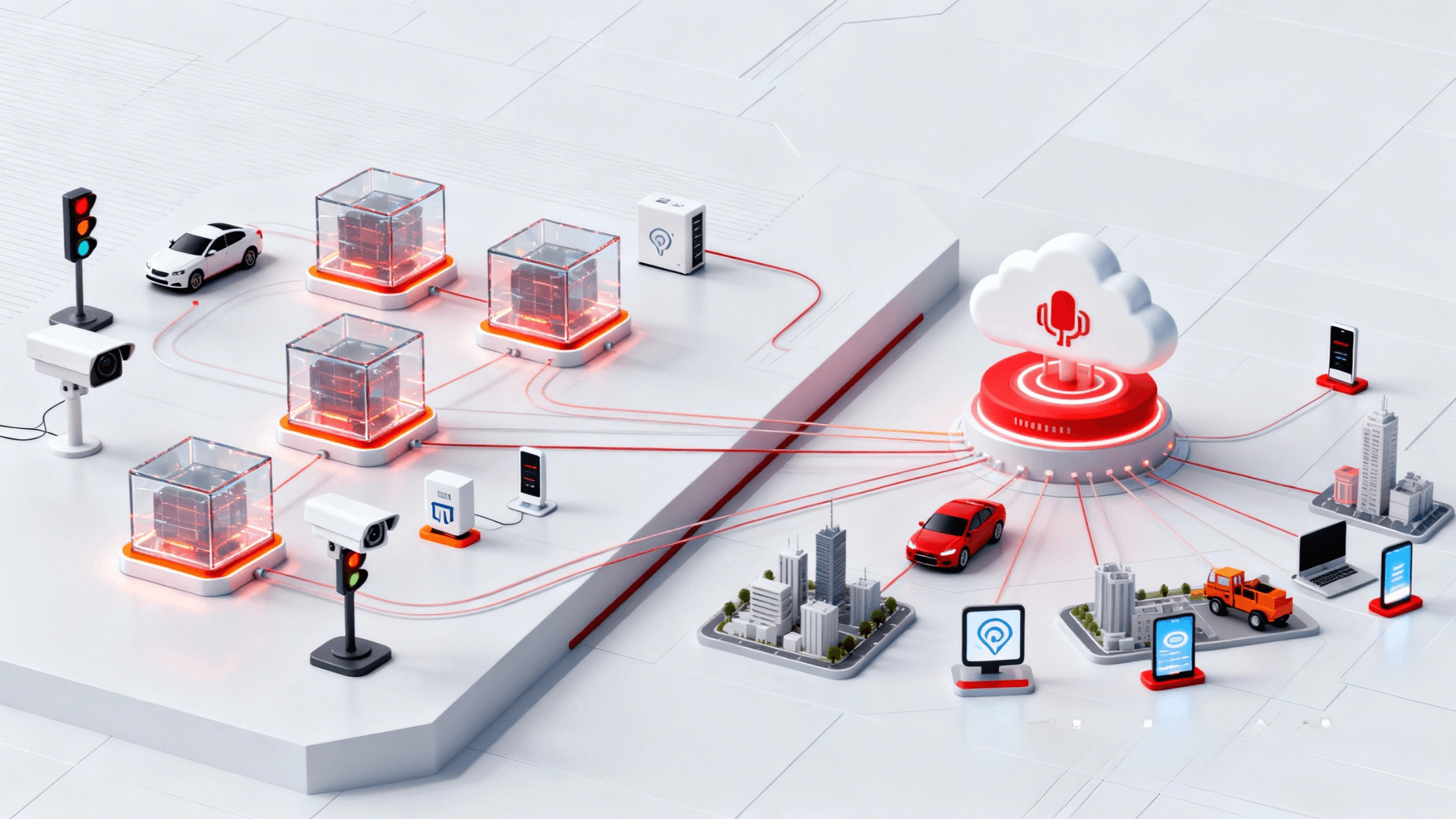
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is the model that processes data at or near the location where it is generated—such as on IoT devices, sensors, cameras, or local systems. Instead of sending all data to a remote centralized data center for processing, edge computing enables analysis and response right at the source.
.jpg)
This approach dramatically reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and ensures sensitive data never needs to traverse the public internet. Today, edge computing is widely adopted in healthcare, smart manufacturing, transportation, telecommunications, and real-time AI applications.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery model that provides on-demand computing resources, such as servers, storage, networking, and software over the internet. Businesses avoid heavy upfront capital investment in physical infrastructure and pay only for what they use.
.jpg)
According to Gartner, cloud computing is “a style of computing in which scalable and elastic IT-related capabilities are provided as a service using Internet technologies.” Common deployment models include Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, and Community Cloud.
Key benefits of Cloud Computing for businesses
In an environment where organizations must optimize costs, accelerate deployment, and scale IT systems flexibly, cloud computing has become the preferred choice for many. It delivers tangible advantages that support efficient operations and long-term growth.
- Low initial capital investment: No need to purchase servers, storage hardware, software licenses, or build and maintain private data centers. The cloud provider handles the entire infrastructure, significantly reducing upfront costs and financial risk.
- Flexible, pay-as-you-go pricing: Businesses pay only for the actual resources consumed (CPU, RAM, storage, bandwidth), avoiding waste from idle capacity common in traditional on-premises setups.
- Unlimited scalability: Resources can automatically scale up or down based on demand. During traffic spikes or project expansion, capacity can be increased instantly without disrupting operations, ensuring consistent user experience.
- Simplified management: The cloud provider manages hardware maintenance, software updates, and incident resolution. Internal IT teams can focus on core activities such as product development, service optimization, and business support.
- High reliability: Data is replicated and backed up across multiple geographically distributed data centers, minimizing data loss risk and enabling rapid recovery from failures.
- Rapid deployment: New servers and applications can be provisioned in minutes, dramatically shortening time-to-market and enabling faster response to business opportunities.
By optimizing costs, enabling elastic scaling, and delivering stable operations, cloud computing not only solves immediate IT infrastructure challenges but also provides a solid foundation for innovation and sustainable growth in the digital age.
Key benefits of Edge Computing
For systems that demand instant response and local data processing, edge computing is increasingly prioritized. It excels in scenarios requiring ultra-low latency, high accuracy, and strict data control.
- Ultra-low latency: Processing occurs at the data source, eliminating or minimizing round-trip transmission to a central location. This enables near-instantaneous responses—critical for real-time AI applications such as image recognition, video analytics, autonomous robots, and smart device control.
- Reduced bandwidth and transmission costs: Only essential aggregated or summarized data is sent to the cloud or central systems, lowering network load, cutting data transfer expenses, and optimizing overall operational costs.
- Higher AI model accuracy: Edge processing preserves full data fidelity—no compression or downsampling is required to fit bandwidth constraints. This results in higher-resolution images, complete video frames, and full sampling rates, leading to more accurate and reliable AI inferences.
- Operation in low- or no-connectivity environments: Edge systems function independently within local networks, making them ideal for remote factories, construction sites, rural areas, or mobile assets with unreliable internet.
- Stronger data sovereignty and privacy: Data remains within the enterprise’s internal perimeter—behind firewalls and existing security layers—reducing exposure to external threats, minimizing attack surface, and supporting stricter compliance requirements.
With real-time processing, minimal latency, and enhanced local data control, edge computing is the ideal choice for high-speed, high-precision, mission-critical systems. It empowers organizations to achieve peak operational performance and prepare for next-generation technologies.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing: Head-to-Head comparison
The table below summarizes the key differences across critical dimensions—processing location, latency, scalability, cost, and application fit—to help you quickly evaluate which model aligns best with your requirements.
| # | Criterion | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
| 1 | Operation | Data processed and responded to locally at source | Data transmitted over internet to remote processing |
| 2 | Deployment Location | Near data source, at network edge or end devices | In remote data centers or centralized server clusters |
| 3 | Latency | Very low (processed close to source) | Higher (depends on data travel to central location) |
| 4 | Response Time | Microseconds – ideal for real-time | Up to seconds – network-dependent |
| 5 | Internet Dependency | Minimal or none | High – requires stable internet connectivity |
| 6 | Real-Time IoT | Excellent fit for real-time IoT and AI | Not suitable for strict instant-response scenarios |
| 7 | Architecture | Local caching, short-term storage, basic analytics | Big data, complex analytics, long-term storage |
| 8 | Security | Higher – data stays local, limited network exposure | Lower – data transmitted and stored remotely |
| 9 | Centralization | Decentralized – closer to users/devices | Highly centralized |
| 10 | Scalability | Strong locally; challenging at massive scale | Globally elastic and virtually unlimited |
| 11 | Cost | Higher upfront (edge hardware/software) | Lower – pay-per-use model |
| 12 | Best-Fit Applications | Manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, real-time systems | Long-term storage, big data analytics, enterprise-wide apps |
Edge computing and cloud computing are not mutually exclusive—they complement each other. Edge excels in low-latency, real-time, and privacy-sensitive use cases, while cloud dominates in global scalability, massive storage, and advanced analytics. Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach to maximize the strengths of both.
When to choose Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. The right choice depends on latency requirements, connectivity, data sensitivity, and operational goals.
When to choose Edge Computing
- Applications demanding near-instantaneous response (microsecond-level latency critical)
- Highly sensitive or regulated data that must remain local
- Environments with unreliable or intermittent internet (remote sites, factories, vehicles)
- Representative use cases: medical robotics, autonomous vehicles, smart factories, real-time IoT
When to choose Cloud Computing
- Long-term, large-scale data storage needs
- Big data analytics, complex AI/ML training, and deep business intelligence
- Elastic scaling to handle variable or growing workloads
- Cost optimization through pay-per-use without heavy CapEx
- Representative use cases: websites, e-commerce platforms, SaaS applications, enterprise systems, centralized AI & big data processing
In summary, edge computing addresses real-time, low-latency, and on-premises control needs, while cloud computing powers elastic scale, long-term storage, and centralized intelligence. In practice, the most effective modern architectures frequently combine both in a hybrid cloud + edge model to achieve optimal performance, cost efficiency, and resilience.
VCLOUD by VNETWORK – Optimized loud Computing solution for businesses
As enterprises increasingly rely on flexible, secure, and high-performance digital infrastructure, selecting a trustworthy cloud platform is critical. VCLOUD from VNETWORK is purpose-built to meet these demands, enabling seamless deployment, efficient operations, and effortless scaling.
.png)
Key Advantages of VCLOUD
VCLOUD is engineered to deliver the highest standards of availability, performance, and security in today’s cloud environments. Here are its standout features:
- 99.997% uptime with Tier III+ certified data centers: Operates on world-class Tier III+ infrastructure, ensuring near-continuous availability and minimal service disruption risk.
- High-performance storage with over 800,000 IOPS: Delivers exceptional read/write speeds, perfectly suited for high-traffic websites, e-commerce, enterprise applications, AI, and big data workloads.
- Multi-layered security compliant with ISO 27001: Includes Firewall, Security Groups, 2FA, SSH Key authentication, continuous monitoring, and international-standard information security practices.
- Automatic resource scaling on demand: Easily adjust CPU, RAM, and storage in real time without downtime, ideal for websites, SMEs, e-commerce, AI & big data use cases.
- 24/7/365 technical support with rapid response: Dedicated VNETWORK engineers provide round-the-clock assistance, allowing your team to focus on business growth rather than infrastructure concerns.
With international-grade infrastructure, superior performance, robust security, and elastic scalability, VCLOUD by VNETWORK is the ideal cloud platform for digital transformation. It delivers cost efficiency, operational stability, and a future-ready foundation for secure, flexible, and sustainable IT growth.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about edge computing and cloud computing
1. What is the biggest difference between edge computing and cloud computing?
The core distinction is data processing location: edge processes data near its source for minimal latency, while cloud processes it in remote centralized data centers over the internet.
2. Should small businesses use edge computing?
Only if they have real-time processing or highly sensitive local data needs. In most cases, cloud solutions like VCLOUD offer better cost savings and simpler deployment.
3. Can cloud computing meet high security requirements?
Yes, especially on platforms that meet international standards. VCLOUD complies with ISO 27001, integrates firewall, security groups, 2FA, and 24/7 monitoring to protect enterprise data.
4. Can edge computing completely replace cloud computing?
No. Edge is ideal for local real-time processing, but cloud remains essential for long-term storage, big data analytics, and centralized management.
5. Which infrastructure models does VCLOUD support?
VCLOUD excels in pure cloud and hybrid cloud scenarios. It allows businesses to combine edge processing at the perimeter with centralized cloud resources for optimal performance, cost, and security.