1. What is spoofing? A complete overview of online impersonation
In cybersecurity, spoofing refers to any technique where an attacker masquerades as a legitimate, trusted entity to trick victims into surrendering data, money, or access. These attacks almost always combine technical manipulation with social engineering, exploiting trust, fear, or lack of technical awareness.
.jpg)
Spoofing is not limited to a single communication channel. It can occur via email, websites, phone numbers, IP addresses, and many other technologies. Any time a malicious actor falsifies their identity to manipulate user behavior or extract information, it qualifies as spoofing.
The consequences of successful spoofing attacks range from personal data theft and network compromise to malware infection, ransomware deployment, and large-scale enterprise data breaches.
2. Common types of spoofing attacks
2.1. Email spoofing
One of the most widespread attacks today. Attackers forge the sender address so the message appears to come from a colleague, executive, bank, or reputable organization. These emails typically request urgent money transfers, system access, or ask recipients to open malicious attachments.
- How it works: Attackers manipulate email headers to display a trusted sender address. When combined with sophisticated social engineering, victims are convinced to take seemingly reasonable actions such as transferring funds, sharing credentials, or opening infected files.
- Potential risks: Consequences can be devastating. Victims may suffer financial loss, expose sensitive data, or inadvertently install malware. Once inside, attackers often escalate to broader system compromise and advanced persistent threats.
2.2. IP spoofing
Attackers forge source IP addresses in packet headers to bypass access controls, launch DDoS attacks, or appear as a trusted internal host.
2.3. Website spoofing / URL spoofing
Creation of fake websites that visually mimic legitimate ones (same logos, layout, domain lookalikes) to capture login credentials or deliver malware. Often distributed via spoofed emails.
2.4. Caller ID / Phone spoofing
Using VoIP services to falsify caller ID, making calls appear to originate from trusted contacts, banks, or authorities to extract information verbally.
2.5. SMS / Text message spoofing
Forging the sender ID in text messages, usually containing phishing links (smishing) or malicious attachments.
2.6. ARP spoofing
In local networks, attackers poison ARP tables to associate their MAC address with a legitimate IP, enabling man-in-the-middle interception or disruption.
2.7. DNS spoofing
Corrupting DNS records to redirect users to malicious sites for credential theft or malware delivery.
2.8. GPS spoofing
Broadcasting fake GPS signals to mislead navigation systems in vehicles, ships, drones, or location-based apps.
2.9. Facial spoofing
Using photos, videos, or 3D masks to bypass facial recognition systems. Mitigated by liveness detection requiring blinks or movement.
3. Why email remains the top target for attackers
Email is the primary business communication channel, carrying financial details, contracts, credentials, and internal discussions. This makes it the ideal entry point for attackers aiming to infiltrate systems or defraud users:
- Default trust in email: Users instinctively trust messages from colleagues, partners, or known brands, lowering their guard against sophisticated impersonation.
- Easy to execute, hard to detect: Changing headers or registering similar-looking domains requires minimal effort. Many attacks contain no malware at all, relying purely on psychological manipulation.
- Gateway to the enterprise: One compromised inbox can trigger supply-chain attacks, ransomware distribution, or full network takeover. Email is often the initial vector in advanced persistent threat (APT) campaigns.
- Traditional defenses fall short: While SPF, DKIM, and DMARC help, modern attackers combine AI-generated content and advanced social engineering to bypass them.
4. Email spoofing: Risks and practical countermeasures
Email spoofing remains one of the most prevalent and damaging threats today, causing direct financial loss, data breaches, and malware infection.
.png)
Key statistics highlight the urgency:
- 91% of ransomware begins with a malicious email
- 62% of APT campaigns use email as the entry vector
- 90% of high-risk emails contain no malware, relying purely on deception
Basic mitigation steps every user and organization should take:
- Use reputable email providers with strong default protections
- Enforce complex, unique passwords and regular rotation
- Enable aggressive spam and phishing filters
- Inspect email headers when something seems off
- Never click links or open attachments from unknown or unexpected sources
- Conduct regular employee security awareness training
While helpful, these measures alone cannot stop determined attackers. This is where VNETWORK’s EG-Platform provides enterprise-grade, AI-powered protection.
5. EG-Platform: The world’s only AI/ML-powered email security solution fully compliant with ITU-T X.1236
EG-Platform is the only email security platform globally that achieves 100% compliance with the International Telecommunication Union’s ITU-T X.1236 standard. Built from the ground up with artificial intelligence and machine learning, it delivers complete bidirectional protection (inbound and outbound) against every modern email threat.
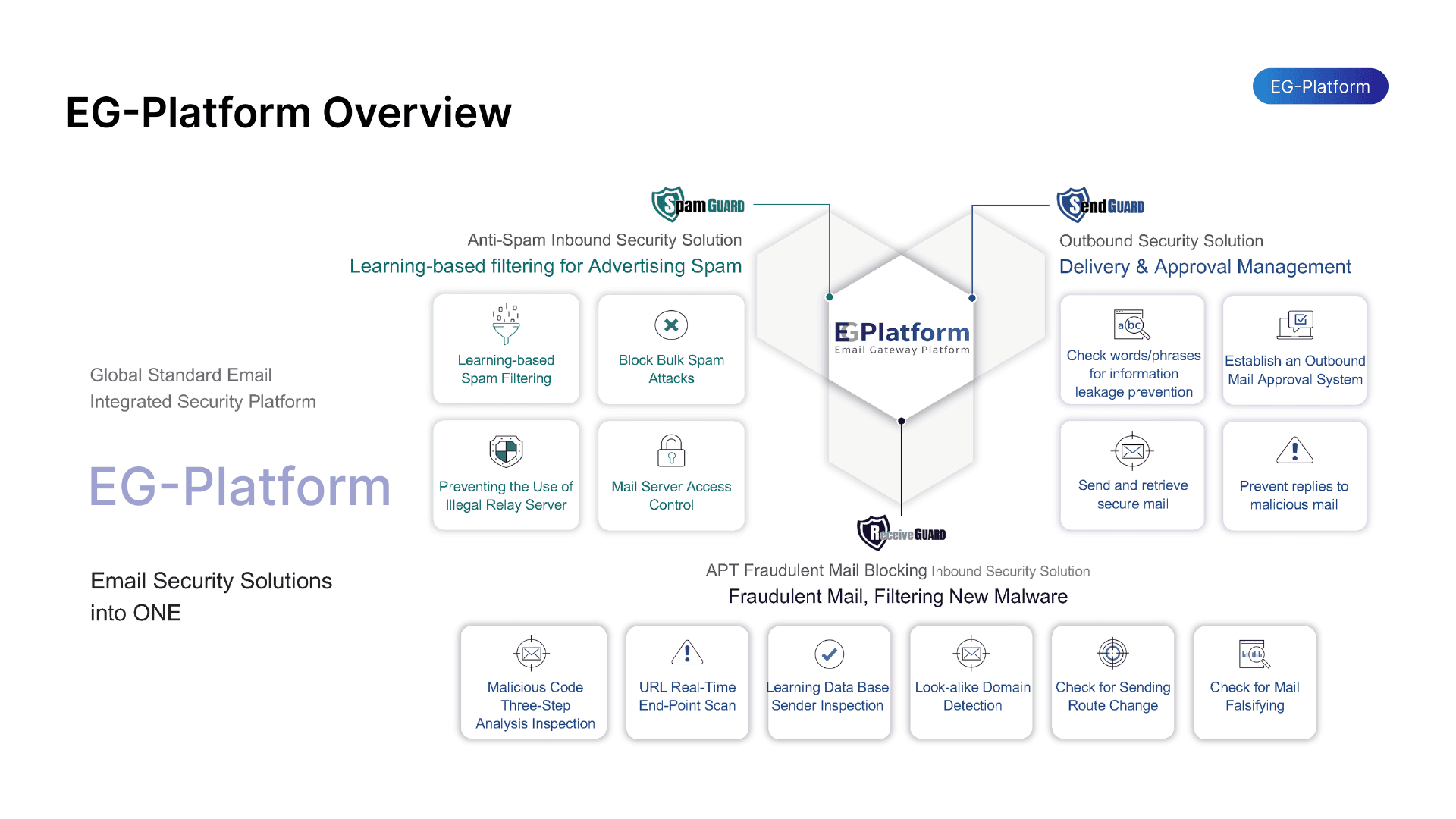
EG-Platform operates a unique triple-layer architecture that inspects, blocks, and remediates threats across the entire email lifecycle:
- Layer 1: SpamGUARD Uses machine learning and Bayesian filtering combined with real-time SPF, DKIM, and DMARC validation to score and block spam, phishing, and ransomware before they reach inboxes.
- Layer 2: ReceiveGUARD Detonates attachments and URLs in isolated virtual environments, performs static and dynamic malware analysis, validates sender reputation, and converts suspicious links into safe images. Historical behavior comparison helps identify sophisticated impersonation attempts.
- Layer 3: SendGUARD Prevents data exfiltration and outbound abuse by scanning content, blocking risky destinations by IP/country/behavior, enforcing keyword filters, requiring approval workflows, and adding password protection to sensitive messages.
6. Why enterprises choose EG-Platform
In an era of increasingly sophisticated attacks, traditional tools are no longer sufficient. EG-Platform delivers proactive, AI-driven defense that adapts in real time.
Key reasons organizations worldwide adopt EG-Platform:
- Dramatically reduces financial loss and data breach risk from email spoofing
- Provides true end-to-end protection across inbound and outbound mail flow
- Continuously evolving AI models that learn user behavior and new threats instantly
- The only solution worldwide with 100% ITU-T X.1236 compliance, endorsed by ITSCC, Gartner, and Rapid7
VNETWORK’s EG-Platform ensures businesses can communicate confidently while staying protected against even the most advanced impersonation attacks.
7. Conclusion
Spoofing comes in many forms: email, website, phone, IP, and beyond. Among them, email spoofing remains the most common and damaging vector.
With VNETWORK’s EG-Platform, organizations gain a modern, AI-powered email security platform that fully complies with the global ITU-T X.1236 standard. It protects the entire email lifecycle (receive, send, and store) against spoofing, phishing, ransomware, and advanced threats.
Let EG-Platform secure your communications, minimize risk, and safeguard your business value in today’s digital world.
FAQ: Common questions about spoofing
1. What is spoofing?
Spoofing is the act of falsifying an online identity (email, website, phone number, IP, etc.) to deceive victims into revealing data or money.
2. How dangerous is email spoofing?
Extremely dangerous. It can lead to direct financial loss, data leaks, and malware infection. Spoofed emails often appear to come from trusted colleagues or organizations.
3. How can I detect email spoofing?
Inspect email headers, verify sender authenticity, avoid clicking unknown links or attachments, enable strong spam filters, and use reputable providers.
4. What are other types of spoofing besides email?
IP spoofing, website spoofing, caller ID spoofing, SMS spoofing, ARP spoofing, DNS spoofing, GPS spoofing, and facial recognition spoofing.
5. How does EG-Platform protect email?
Using multi-layered AI, it blocks 17 inbound and 12 outbound attack types, provides detailed reporting, and is the only solution worldwide fully compliant with ITU-T X.1236.
