What is Load Balancing?
Load Balancing is a mechanism that distributes user traffic across multiple servers within a system, rather than relying on a single server to handle all requests. By evenly sharing the load, Load Balancing ensures system stability, minimizes the risk of overload or downtime, and maintains fast response times, delivering a smooth experience for users.
In the context of e-commerce, media, and tech startups facing escalating traffic volumes, Load Balancing becomes a critical solution. It optimizes performance, enhances fault tolerance, and enables easy scalability while integrating security measures to counter threats like DDoS attacks, ensuring services remain available and secure.
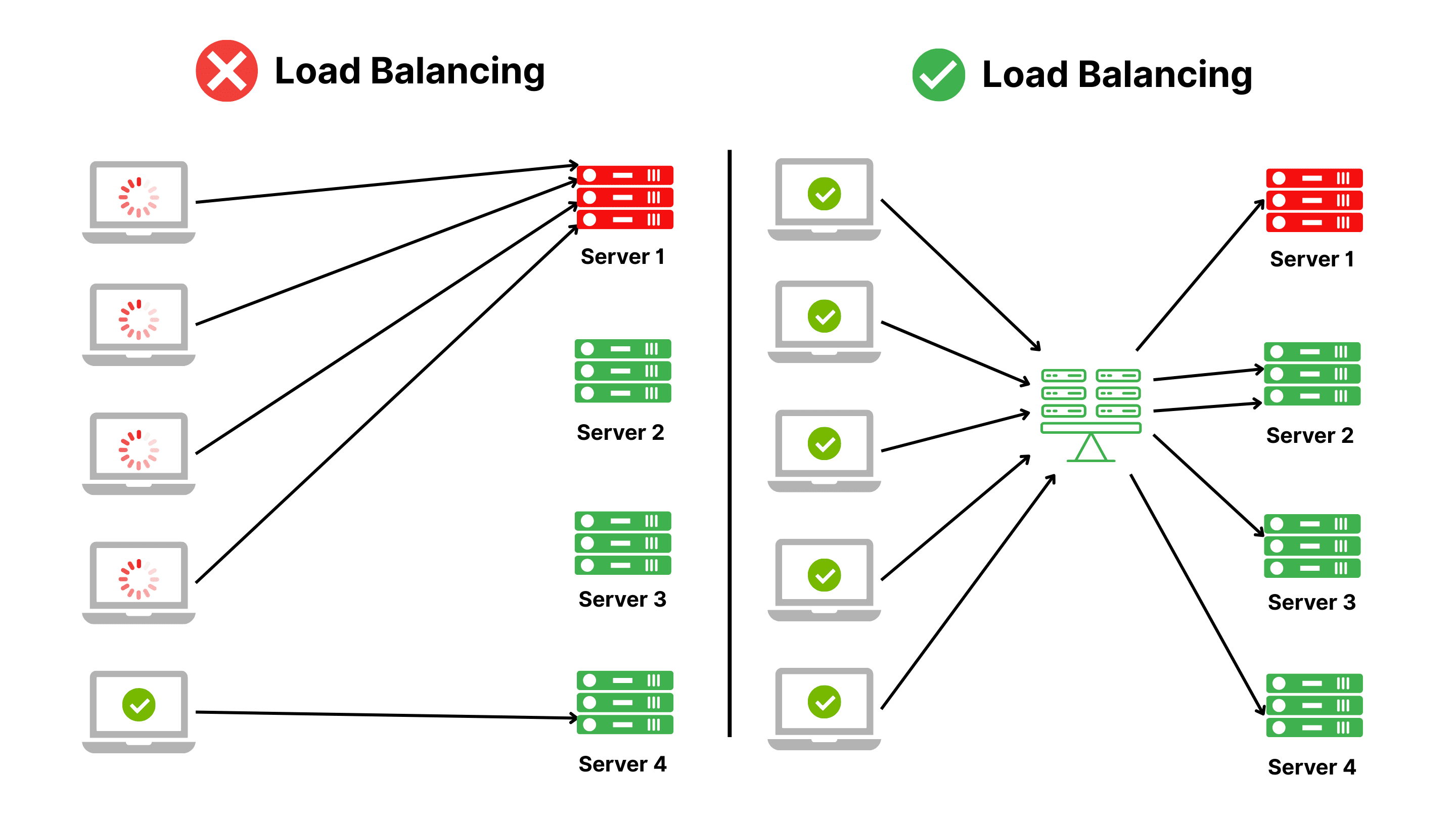
How does Load Balancing work?
Load Balancing operates as an intelligent "coordinator," serving as an intermediary between users and the backend system. Its primary role is to efficiently distribute client requests across servers, optimizing resources and maintaining high performance. Below are the specific steps of how Load Balancing functions:
- Receiving requests: The Load Balancer collects all access requests from users, such as when they visit a website or use an application.
- Identifying the optimal server: Using Load Balancing Algorithms, the Load Balancer assesses server conditions (CPU, RAM, connection count) to select the least busy or most capable server.
- Distributing requests: Requests are routed to the appropriate server, ensuring no single server is overwhelmed while others remain idle.
- Maintaining stable performance: The Load Balancer continuously monitors and adjusts traffic flow, ensuring optimal system performance and supporting availability even if a server fails.
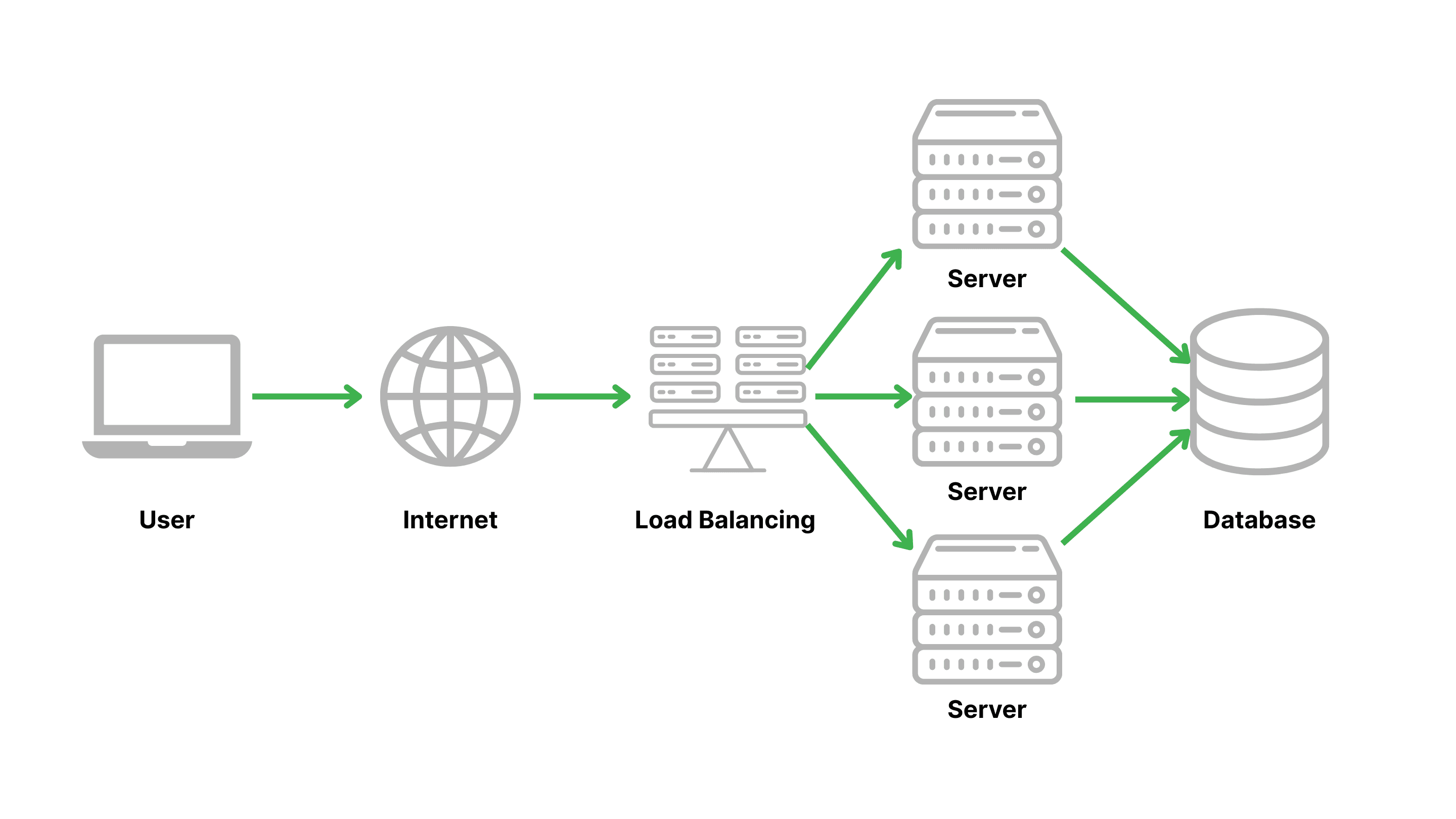
This mechanism not only optimizes system resources but also enhances availability and fault tolerance. For instance, if a server fails, Network Load Balancing automatically redirects traffic to other servers, preventing service interruptions. This ensures businesses maintain performance and deliver a seamless experience, regardless of sudden traffic spikes or unexpected issues.
Benefits of Load Balancing
By intelligently distributing traffic, Load Balancing improves performance, reliability, and scalability of systems. Here are the standout benefits this technology offers:
- Optimized Performance: Network Load Balancing evenly distributes traffic across servers, preventing "bottlenecks" when a server is overloaded. This ensures swift processing, especially during peak hours for e-commerce or fintech platforms.
- Minimized Downtime: When a server fails, Load Balancing automatically redirects traffic to other servers, maintaining availability and reducing downtime—crucial for uninterrupted user services.
- Enhanced Scalability: Load Balancing allows businesses to add or remove servers without service disruption, making it ideal for growing enterprises.
- Improved Security: Load Balancers can integrate with solutions like Cloud WAF to mitigate attacks such as DDoS, SQL injection, or other cyber threats, keeping systems secure.
- Smooth User Experience: With fast and stable response times, Load Balancing reduces bounce rates, boosts customer satisfaction, and retains users.
These benefits make Load Balancing an indispensable tool, supporting tech startups to large corporations in maintaining efficient and reliable IT systems. Combined with solutions like DNS Load Balancing, businesses can optimize global user experiences, meeting the rising demands of the digital age.
Load balancing algorithms
Load Balancing Algorithms, also known as Load Balancing Algorithms, are a set of methods used to efficiently distribute traffic, ensuring smooth system operation and resource optimization. These algorithms are categorized into two main types: Static Load Balancing Algorithms and Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithms, each suited to different system scenarios and requirements.
Static load balancing algorithms
Static Load Balancing Algorithms distribute traffic based on fixed rules, independent of real-time server conditions:
- Round Robin: Routes requests sequentially to each server in a circular pattern, ensuring fairness. This simple, effective method suits systems with uniformly performing servers, commonly used in Network Load Balancing.
- Least Connections: Prioritizes servers with the fewest active connections, ideal for systems with varying server capacities to prevent overloading weaker servers.
- Hashing: Distributes requests based on user IP or session, maintaining session stability. This approach is often applied in DNS Load Balancing to keep users connected to the same server.
Dynamic load balancing algorithms
Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithms offer greater flexibility, adjusting traffic distribution based on real-time system conditions:
- Weighted Round Robin: Allocates more requests to stronger servers based on predefined weights, suitable for systems with performance disparities.
- Adaptive Load Balancing: Automatically adjusts distribution using metrics like CPU, RAM, or bandwidth, optimizing performance in complex environments like Global Server Load Balancing across multiple data centers.
- Response Time Algorithm: Selects the server with the fastest response time to handle requests, ideal for low-latency applications like e-commerce or streaming.
Types of Load Balancing
Load Balancing varies depending on system needs and characteristics. Below are the common types:
Application load balancing
Operating at the application layer (Layer 7 – HTTP, HTTPS), Application Load Balancing focuses on request content. It suits websites, APIs, or e-commerce platforms, analyzing request details to make smart routing decisions, such as prioritizing servers for specific content (images, videos), ensuring a seamless experience.
Network load balancing
Network Load Balancing handles traffic at the network layer (Layer 4 – TCP/UDP) in the OSI model, emphasizing high performance and low latency. It is ideal for speed-critical applications like streaming, online gaming, or real-time services, ensuring stability during traffic surges by distributing based on network protocols.
Global server load balancing (GSLB)
Global Server Load Balancing distributes traffic across data centers in multiple countries, optimizing global performance. Using Load Balancing Algorithms, it directs requests to the nearest or least-loaded data center, ensuring speed and reliability for international users. This is a hallmark of solutions like VNETWORK’s CDN with over 2,300 PoPs.
DNS load balancing
DNS Load Balancing uses the DNS system to route users to the geographically nearest server based on their location. It suits businesses needing wide traffic dispersion, such as global e-commerce or content platforms, reducing latency and enhancing user experience by connecting them to the optimal server.
Hardwar & Software load balancers
Load Balancing can be implemented through two primary technologies: Hardware Load Balancers and Software Load Balancers. Each offers unique advantages, catering to different business sizes and needs, from large organizations to tech startups.
Hardware load balancers
- Characteristics: Hardware Load Balancers are specialized physical devices designed for high performance and exceptional stability, typically integrated into data centers for large traffic volumes.
- Applications: Ideal for large organizations like banks, e-commerce corporations, or online news platforms requiring Network Load Balancing for high traffic.
- Advantages: Delivers stable performance, fast processing, and reliability, especially for global traffic distribution.
- Disadvantages: High initial investment (CAPEX) and operational/maintenance costs (OPEX), requiring skilled technical teams for management.
Software load balancers
- Characteristics: Software Load Balancers are installed on servers or cloud environments, offering flexible deployment and easy scalability.
- Applications: Perfect for small to medium-sized businesses, especially those using cloud or hybrid models.
- Advantages: Lower costs, high flexibility, and easy integration for geographic traffic optimization.
- Disadvantages: Performance depends on cloud or server infrastructure, potentially lacking the stability of hardware in extreme traffic scenarios.
Comparison of Hardware load balancers and Software load balancers
| Criteria | Hardware Load Balancers | Software Load Balancers |
| Cost | High (CAPEX + OPEX) | Lower, subscription-based |
| Flexibility | Limited, device-dependent | Flexible, easily scalable |
| Performance | High, stable, optimized for large traffic | Depends on cloud/server infrastructure |
| Deployment | On-premise | Cloud or Hybrid |
AI Smart Load Balancing by VNETWORK
AI Smart Load Balancing by VNETWORK is an advanced solution that leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize the Load Balancing process. This system employs machine learning algorithms to analyze real-time data, predict traffic peaks, and automatically adjust traffic distribution based on user behavior, geographic location, and server status. This significantly reduces latency and enhances availability, making it ideal for e-commerce, media, or tech startups facing sudden traffic surges.
Integrated with VNCDN—a robust CDN infrastructure by VNETWORK featuring over 2,300 PoPs and 2,600 Tbps bandwidth across 146+ countries—AI Smart Load Balancing ensures intelligent routing to the most optimal servers. Additionally, it integrates with VNIS Cloud WAF to mitigate threats like DDoS at the entry point, providing comprehensive security. With its automation and scalability, this solution serves as a strategic tool for businesses to maintain high performance and sustainable growth in the digital era.
Conclusion
In the digital age, Load Balancing is more than a technical tool—it is a foundation for optimizing performance, security, and scalability of IT systems. With innovative solutions like AI Smart Load Balancing and VNCDN’s coverage across 146+ countries, VNETWORK delivers comprehensive solutions for all needs, from e-commerce to tech startups. Contact VNETWORK today for expert consultation and to implement the optimal solution for your business!
FAQs
1. What is Load Balancing and why is it important?
Load Balancing is a mechanism that distributes traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload and ensure performance. It is vital for reducing downtime, boosting speed, and maintaining a smooth user experience, especially during traffic spikes.
2. How do Hardware Load Balancers and Software Load Balancers differ?
Hardware Load Balancers are physical devices with high performance but high costs, suited for large organizations. Software Load Balancers are flexible, cost-effective, and ideal for small to medium businesses, especially in cloud or hybrid environments.
3. How does AI Smart Load Balancing by VNETWORK work?
AI Smart Load Balancing by VNETWORK uses artificial intelligence to analyze real-time data, predict traffic peaks, and intelligently distribute traffic, integrated with VNCDN for enhanced performance and security.
4. Can Load Balancing protect systems from DDoS attacks?
Yes, Load Balancing disperses traffic across multiple servers, reducing the load on any single point and minimizing risks during large-scale DDoS attacks, especially when integrated with VNIS Cloud WAF for added protection.
5. Do small businesses need Load Balancing?
Yes, Software Load Balancers offer a cost-effective option, helping small businesses optimize website performance, reduce load times, and improve user experience even during traffic increases.
6. Can Load Balancing reduce infrastructure costs?
Yes, instead of investing in an expensive high-capacity server, businesses can use multiple smaller servers with Load Balancing to distribute traffic, saving costs while allowing easy scalability.
7. Is Load Balancing necessary for e-commerce websites?
Yes, e-commerce sites often face simultaneous access during flash sales or holidays. Load Balancing ensures traffic distribution, prevents congestion, and guarantees a smooth shopping experience.
8. My website slows down with high traffic—can Load Balancing help?
Yes, Load Balancing evenly distributes traffic across servers to prevent slowdowns. With VNETWORK’s Multi CDN solution, the system automatically adjusts to maintain speed during peak times.